
NASA also run the INSPIRE project and offer a VLF Receiver kit - the VLF-3 which is more orientated towards listening for the ‘natural radio’ effects caused by the interaction of lightning and the earth’s magnetic field.Īll these receivers require a device to convert the analogue signal to a digital signal that the computer can understand.
Vlf receiver review full#
The UKRAA also offer a full range of assembled modules (including pre wound aerials) so that it really is a case of simply plugging together a series of modules and perform some basic tuning and you are away. Finally, the 3rd option is to buy a ready assembled unit. The UKRAA offer a kit or alternatively, constructional detail for a simpler design, the Gyrator II is available from the AAVSO.ģ. Not really a feasible option for a total beginner, but if you have constructed an electronic kit of some sort then this is a valid option. The detector stage converts the amplified signal to a direct current that is then recorded (along with a time stamp) at the PC.Ģ. The amplifier stages magnify the received signal to something that can be worked with. The filter discriminates and selects only the signal that you want to observe. Generally, the bigger the aerial (tuned to the correct freqency), the more radiation that is collected. There are 5 basic components, an aerial which collects the radiation.

The architecture of a VLF receiver is essentially the same as for all types of receivers. Ideally, a dedicated VLF receiver should be acquired, and there are a number of options. It is possible to record the output from these applications, but they are not ideal for long term logging and analysis of solar events, however, some observers do just this and make very useful observations.
Vlf receiver review software#
The output from this type of software is a sample of a radio spectrum (limited in this case by the capability of the sound card) up to a maximum frequency of about 20kHz.

Use a 'waterfall' application such as Spectrum Lab available from Īn easier to use (but less feature rich) alternative is Spectran, available from
Vlf receiver review Pc#
There are a few options for getting started.Īs explained, one very easy option is to simply connect a loop antenna directly into the Line In input on a PC Sound Card. There is an active group of observers recording SIDs with John Cook compiling a monthly summary report. New observers are always welcome and if you wish to participate please contact the Section Director This shows an enhanced signal from 2 transmitters (one local UK (red) and the other (blue) in France). The example trace shown is of an M8.3 class flare that occurred on. In some cases, the signal can completely disappear, particularly with strong ‘X’ class flares. When a solar flare occurs, the radiation from the sun affects the ‘D’ layer, causing either an increase in signal or decrease in received signal. During daylight hours the signal strength received from these transmitters remains fairly constant. The transmitted signal is reflected by the ‘D’ layer in the earth’s atmosphere. The receiver is tuned to a remote VLF transmitter (usually operated by the military for submarine communications) about 1000km away. The wire loop feeds a simple amplifier and filter and a DC output is recorded to a chart. The aerial usually consists of a loop of wire – about 120 turns on a 600mm square frame. The electronics are not critical, the aerial is fairly small and reception can even be performed on a PC with NO receiver (by simply connecting an aerial to the sound card). The aim is to observe the impact of solar flares upon the earth’s ionosphere through Sudden Ionospheric Disturbances, or SIDs. Very Low Frequency astronomy is possibly the easiest form of radio astronomy that can be undertaken. It shows that the sensitivity of realized VLF receiver is almost linear in the predefined frequency range for the input signals lower than -12dBm and to be quadratic for the higher level input signals.Thursday, 2019, November 7 - 12:01 VLF Very Low Frequency Observations
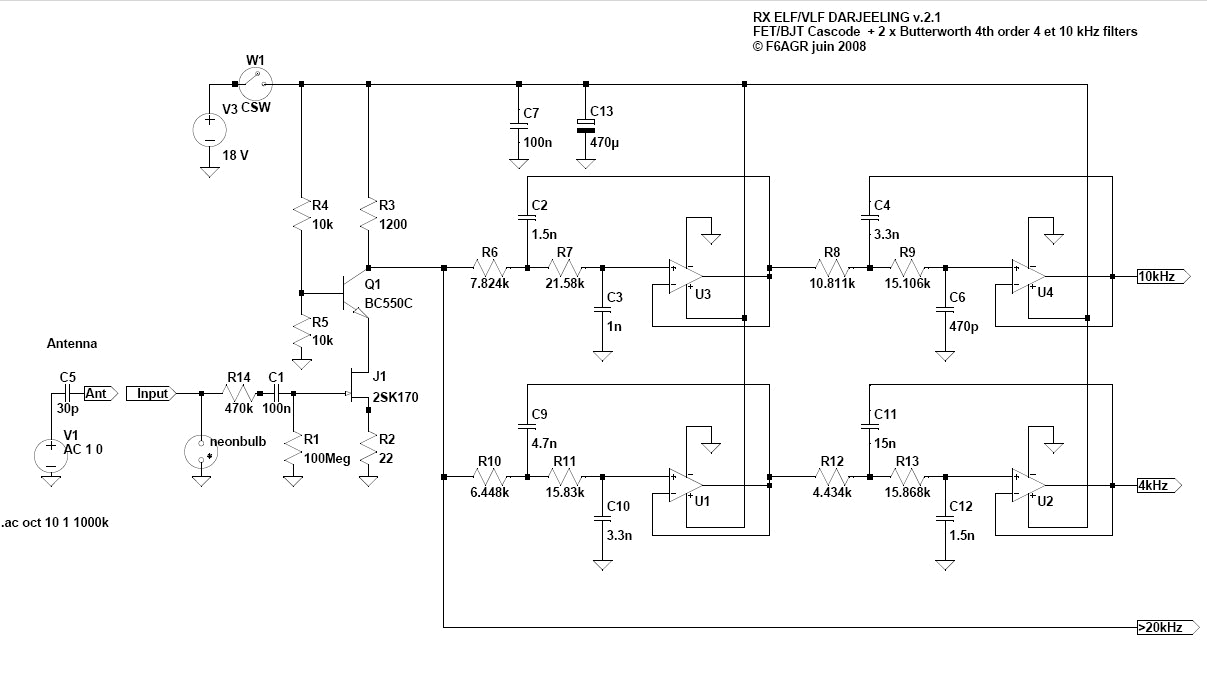
After obtaining the optimum design, the hardware realization is implemented on a printed circuit board (PCB) for experimental characterization. The VLF receiver which is portably designed is also equipped with an output port connectable to the soundcard of personal computer for further data acquisition. The developed receiver is intended to have high sensitivity reception for the signals in frequency range of 10-30 kHz allocated for earthquake observation. In research related natural phenomena such as atmospheric noise, lightning and earthquake, a VLF receiver particularly with high sensitivity is utterly required due to the low power of VLF wave signals received by the antenna. A high sensitivity very low frequency (VLF) receiver is developed based on AD744 monolithic operational amplifier (Op-Amp) for earthquake data acquisition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
